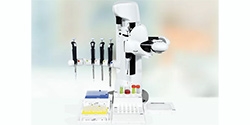
ABB demonstrates concept of mobile laboratory robot for Hospital of the Future
Next-Gen Control System for Prosthetics
Diligent Robotics Announces Market Launch of Moxi and $3M Seed Funding
Training Surgeons to Use Robotic Systems
Bringing Robotic Surgery to Places Where Others Don’t Want to Go
ABB Robotics to Develop Solutions for the Hospital of the Future
Treating Heart Disease with Robotic Precision and Safety
Robotics in Cancer Surgery
Surgical Robots and Their Rapid Adoption in Minimally Invasive Surgeries
The Strangest Reasons We've Seen Robots Engineered For So Far
Robots to Perform Spinal Surgery With Pinpoint Accuracy
Kindred Hospital Rehabilitation Services Purchasing Robots for Stroke Therapy
Automation Advancing the Pharmaceutical Industry
Morphological Approaches in Medical Technology
WPI and Albany Medical College Developing Robotic System to Treat Brain Tumors
Records 31 to 45 of 95
First | Previous | Next | Last
Featured Product